18 October 2022
MAKING DIGITAL GREAT AGAIN: CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE CENTERS
A walk through the changing digital landscape in financial services and how organizations can adopt a dynamic customer experience center.
In the third part of our series, “A Traditional Contact Center vs. a Customer Experience Center,” we explored how customer experience centers (CX centers) contrast with traditional contact centers by placing thoughtful customer journeys and employee engagement at the heart of contact center digital transformation.
To build a truly relationship focused CX center, organizations must reassess their approach toward each of the below four pillars:
Shifting to a digital-first culture means technologies are not simply implemented for the sake of ‘doing digital.’ Instead, solutions are assessed as part of a holistic ecosystem that brings value to customers and employees alike.
A. Digital is a means to an end, not the end goal
Many companies adopt digital solutions just to ‘do digital,’ but that leads to a pile of poorly integrated solutions that add administrative headaches rather than improve customer experience or operational efficiency.
By adopting a digital-first culture, organizations should be assessing digital solutions in the context of customer and employee needs, as well as the organization’s existing people, processes, technologies (PPT), and data.
B. Digital-first is not equivalent to digital-only
One of the most important principles that many organizations forget is that being digital-first does not mean being digital-only. A truly customer-oriented organization views its digital solutions as a building block within a holistic CX center that enables better experiences alongside human channels.
A. Personalize the customer experience
Personalization across every facet of customer engagement is central to modern relationship banking. With increasing amounts of customer data and greater capabilities to process large amounts of data in real-time, personalization will move past the traditional tailored marketing messaging, into much more advanced analytics that addresses both sales and servicing needs.
Within the realm of CX centers, personalization can take on many forms:

B. Proactively identify customer needs
Proactive identification of customer needs allows organizations to support and engage with the customer in a targeted manner, helping financial institutions build lasting relationships with their customers while boosting sales and mitigating issues. As the volume of customer data increases along with the ability to process data quickly, financial institutions will be better positioned to predict customer needs and proactively reach out to the customer instead of reacting to an incoming call from an already frustrated customer.
By identifying these opportunities to address customer needs from the servicing, sales, and advisory perspectives, financial institutions can better position themselves as trusted advisors, paving the path back to relationship banking.
A. Empathize with your customers
Major causes behind failed project deployment often stem from poor communication, uncoordinated management, and unpredicted expenses. To avoid these common pitfalls, an Agile mindset and design thinking practices can help organizations drive innovation through a customer-centric lens.
In practice, this drives an iterative approach to problem-solving where organizations will utilize user feedback to redefine the problem with more accurate solutions. Agile solution delivery will also ensure fewer errors through a more collaborative and adaptable approach.
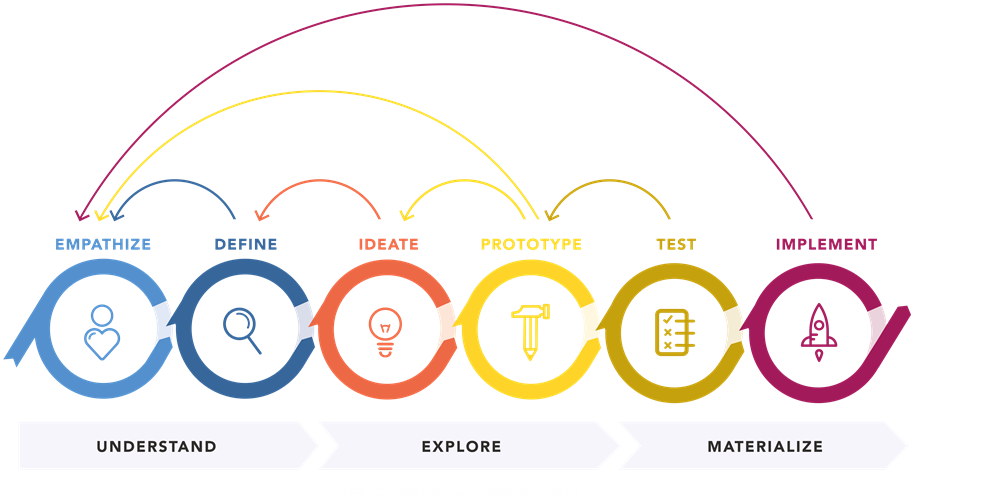
Ultimately, by empathizing with the customer through the process of a design thinking model, an organization will better understand the client’s requirements and develop user-focused solutions.
B. Create a roadmap for small and iterative improvements
While utilizing customer feedback is imperative to the problem-solving process, it is just as important that companies think long-term. An Agile approach will allow for small, targeted changes to be gradually introduced. Combined with integrated feedback, the impact on customer experience will be much greater.
For example, Barclays utilized an Agile mindset to successfully transform their business and maximize efficiencies within their internal operations. Barclays launched a companywide Agile transformation that spanned everything from project management to organizational structure. Using Discipled Agile Delivery, Agile coaching and extensive training were rolled out, helping to simplify processes and improve productivity across the organization. The physical workplace was also modified to facilitate a more collaborative work environment, while the company leadership began taking a more holistic approach, streamlining the end-to-end value stream.
By gradually introducing these changes throughout the organization, Barclays saw a 300% increase per month in stories produced across projects and the lowest level of production incidents on average per month. These benefits have also directly impacted customer experience, as the products saw greater user adoption, and continuous improvement was driven by the banks' ability to pivot quickly based on user feedback.
With the shift in focus on towards customer experience, digital contact centers have adapted emerging technologies to provide omnichannel experiences. Traditional contact center technologies are strengthened with embedded advanced analytical capabilities using AI and ML. Strategies, such as knowledge recommendations and employee segmentations can enable organizations to proactively help customers while supporting a high level of system integration. Some of the key enabler technologies that pave the path towards a CX center include the following:
A. Integrated Service Channels
A digital CX center can provide multiple modes of communication to customers seeking assistance. Customers should be able to switch from one avenue of assistance to the next in a seamless manner. For example, a customer who engages with a chatbot online can call the contact center and get connected to an agent who is already aware of the customer’s inquiry and is prepped to provide the required support.
B. Advanced Customer Self-Serve
With more customers achieving greater digital literacy, demand for digital self-serve options has increased. The latest content management systems have enabled efficient integrated knowledge bases. These systems have online analytical tools that can be leveraged by customers for information and service options. They also have a simplified interface and easy navigation to other service channels like chatbots, plus contact numbers if customers require further assistance.
C. Intelligent Automatic Call Distribution
Intelligent automatic call distribution enables significant improvements to contact center wait times and customer experience.

D. Conversational IVR
Conversational IVR, utilizes voice recognition, AI, and natural language processing. This IVR uses human-like conversations to interact and interpret customer needs.
The technology can be trained to solve standard customer queries and if necessary, seamlessly transfer the call to an active agent who is equipped with the existing customer information via an integrated CRM system.
E. Integrated Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
A CRM is a strategic tool that helps organizations aggregate, organize, and analyze customer information data to manage better customer interactions. An integrated CRM can provide seamless connectivity between the CRM tool and other components of a digital contact center.
Smart integration retrieves the right information from back-end data sources and analytical systems, enabling the orchestration of appropriate workflows across connected channels. Robotic process automation (RPA) can also be used to automate tasks through all the Integrated applications.
F. Unified Agent Desktop (UAD)
A UAD provides a single platform to provide agents with proactive real-time smart assistance, connecting to all other upstream and downstream systems like IVR, CRM or offers recommendation engines.
The increasingly competitive financial services industry, along with the decreasing patience of customers and employees, has made it more necessary than ever to create comprehensive, relationship-focused, assisted digital customer experience channels. Customers are no longer satisfied with basic service through phone channels, and contact center employees are no longer satisfied with repetitive, menial tasks with little professional development.
To stay competitive and retain customer loyalty, large financial institutions must reassess their approach toward sales through self-service and assisted channels, viewing their customers through the lens of an end-to-end relationship rather than a set of disparate transactions.